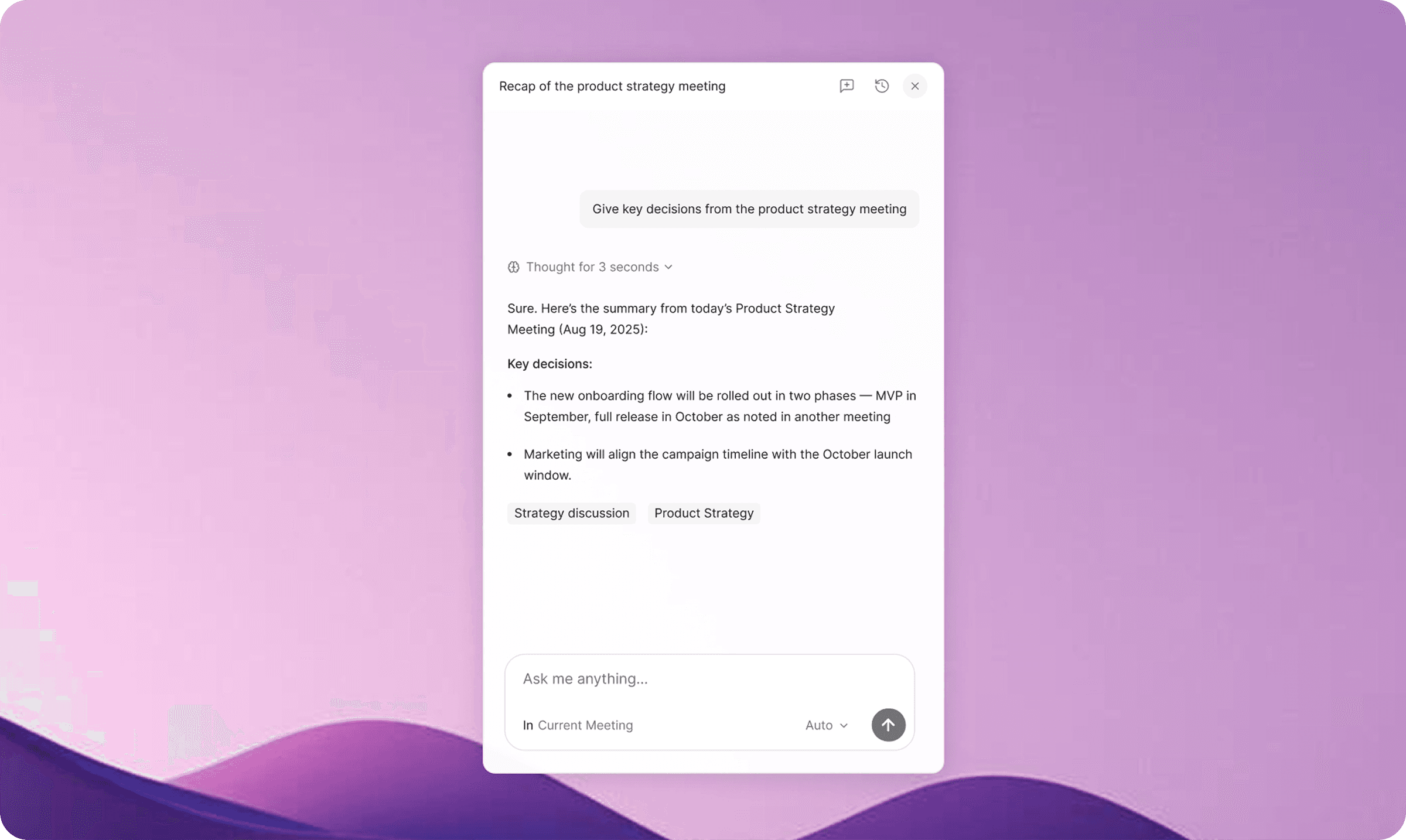
Customer story
How Jamie built an accurate, private meeting intelligence in Europe?
Jamie is an AI meeting assistant that turns conversations into transcripts, summaries, and action items. The product is built around two core principles: no bots in your meetings, and strict GDPR compliance. Users record calls directly (even offline if needed), and all processing happens on-premise in European data centers. Audio files get deleted after transcription.
This matters because Jamie's entire value proposition depends on knowing who said what. If the system assigns “Review the Q3 budget” to the wrong person, the meeting notes become useless. Worse, they become confusing.
Speaker attribution has to be correct because Jamie’s summaries, decisions, and task assignments all break the moment the system assigns the wrong person.
For Jamie's team, diarization isn't a feature. It's the foundation.
“Jamie’s team needed predictable accuracy at scale, and that was exactly where Precision-2 made the difference.”
Egor Spirin
CTO, co-founder @ Jamie
What do their users actually do?
Jamie's use cases are harder than typical meeting recordings:
Offline recordings in noisy environments. Users record lectures and conferences on their phones, often with significant background noise. One recording device, multiple speakers, no control over acoustic conditions.
Large multi-speaker meetings. Meetings with 10+ participants where people interrupt each other and talk over one another. The system needs to track who's speaking even when speech overlaps.
Privacy-sensitive contexts. Users choose Jamie specifically because they don't want a bot on the call or audio stored on external servers. This means the entire pipeline: diarization, transcription, and LLM processing runs on-premise in under two minutes.
Jamie's team described one recording that stood out to them: “We had a meeting with 10 people, phone sitting on the table quite far away. You could barely hear what people were saying, but the speaker attribution was still very good.”
That's the bar. Not clean studio audio with clearly separated speakers, but real-world meeting audio where diarization has to work anyway. These cases are exactly where paynnoteAI Precision-2 held up, staying accurate even when the audio was noisy or speakers overlapped.
The switch to pyannoteAI
Jamie was growing fast, and the open-source model could not keep up with their speed, accuracy, and on-premise demands.
Jamie moved to pyannoteAI's commercial Precision-2 model. The decision came down to three things:
First, it was measurably more accurate. The team saw 20-30% improvement in diarization accuracy compared to the open-source version.
Second, it was faster. Speed matters when you're processing thousands of hours per week, and users expect results in under two minutes.
Third, it could be deployed on-premises: no API calls, no data leaving Europe, full control over the pipeline.
The pyannoteAI team also helped them optimize GPU configuration for their on-premise setup. Jamie's team found this useful as the deployment was challenging, but the guidance on drivers and GPU selection made the process smoother.
What changed after the switch?
The improvements weren't subtle:
Difficult audio scenarios started working. Noisy rooms, distant microphones, and overlapping speech: cases that previously caused attribution errors became reliable.
Support tickets about speaker attribution decreased. The team doesn't track exact numbers, but complaints about incorrect speaker assignment dropped noticeably after switching to Precision-2.
Processing stayed under two minutes. Faster diarization kept the entire pipeline within their delivery window even as customer load increased.
The voice snippet feature became more reliable. When users click to hear who said what, the audio now matches the attribution more consistently.
The team also mentioned the exclusive diarization flag helped in multi-speaker meetings where people talk over each other. Interruptions and crosstalk are standard conditions, not edge cases.
“The real win was reliability at high load because every time attribution failed, downstream features suffered.”
Aleksandr Ogaltsov
AI Scientist @ Jamie
Precision-2 gave them reliable accuracy at scale, which was the main blocker before the switch.
What accurate diarization enables?
With better speaker attribution, Jamie's LLM pipeline functions as intended. Action items get assigned to the right people. Decision summaries attribute statements correctly. Task lists make sense.
Users record meetings with their phones in conference rooms, knowing the system will figure out who said what. They use Jamie for lectures and presentations, trusting that speaker attribution will work even in challenging acoustic environments.
The product promise: accurate meeting intelligence without bots, with full privacy compliance, depends entirely on the diarization layer working correctly. When it fails, everything downstream breaks. The accuracy jump removed most of the failure cases, so the pipeline behaves predictably across all recording types.
What's next
Jamie is pushing toward real-time processing and more flexible diarization variants, and pyannoteAI is aligning its roadmap to support that path. Better coordination between diarization and transcription is also in scope because it helps Jamie handle overlap and larger meetings as they scale.



